Our ultrafast Femtosecond laser here at US Photonics affords us some very crucial advantages over other state-of-the-art laser types. The most notable advantage is the lack of heat transfer during the ablation of a material. Traditional laser machining utilizes laser systems that either operate in a continuous manner or are pulsed on and off on the microsecond (10-6 seconds) or nanosecond (10-9 seconds) timescale. Although these pulses may seem short, they are actually quite long when compared with the time frame of heat absorption (picosecond or 10-12 seconds). If the pulse of light is longer than the timescale of heat transfer, thermal damge may occur resulting in cracking, slag recast, and crystal structure rearrangement. |
 US Photonics supplied matches whose heads were engraved with our Femtosecond Laser for use as the Fall 2009 cover of Micro Manufacturing Magazine. US Photonics supplied matches whose heads were engraved with our Femtosecond Laser for use as the Fall 2009 cover of Micro Manufacturing Magazine.
|
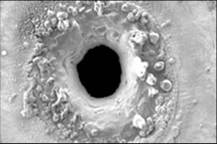
Conventional laser machining with microsecond and nanosecond lasers imparts excess heat into the sample material causing recast of slag, microcracking, and jagged features (Pictured Above). Additional post processing is necessary to clean the surface and smooth the features out. |
Femtosecond or Ultrafast lasers are three orders of magnitude shorter than the timescale of heat absorption (10-15 seconds vs. 10-12 seconds). In this way, femtosecond laser machining avoids the thermal damage associated with traditional machining techniques (laser, EDM, hard tool, etc.) and has the ability to cleanly ablate materials that would otherwise melt, crack or fracture, and even has the ability to ablate highly flamable materials such as the head of a match.
Drawbacks of Conventional Laser Machining Techniques:
- Residual heat and stress around machined area
- Cracking
- Splatter and slag recast
- Sub-surface stress fractures
- Limited to metallic materials
- Feature sizes on the tens of microns
Advantages of Femtosecond Laser Machining:
- Time scale for heat absorption is on the psec scale (10-12)
- Femtosecond laser pulse is 10-15 seconds
- Material is ablated and ejected before residual heat is imparted into the sample:
- No damage to adjacent material
- No splatter or slag recast
- No heat affected zones
- No sub-surface stress fractures
- Sub-micron feature sizes
Are there any disadvantages to femtosecond laser machining?
Due to the precision of the laser and size constraints of the material, Femtosecond laser machining is more time consuming than traditional laser machining. We have, however, discovered several proprietary methods for decreased processing times. |

